Types of contraception
There are various things to be considered when women, men, or couples decide their preferred choice of contraception. These include effectiveness, affordability, accessibility, and safety. It is advised that when choosing an effective method of contraception, dual protection from HIV and other transmitted diseases along with unintended pregnancy should be considered.
Various contraceptive methods have been described below:
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
Copper ‘T’ IUD is a long-acting reversible contraceptive. It is a small ‘T’-shaped device consisting of a plastic frame with copper wire wound around, that is placed inside the uterus. It is used as birth control and an emergency contraceptive if inserted within 5 days of unprotected sex.
With a failure rate of 0.7%, it is one of the most effective methods of contraception. It acts by killing the sperm and preventing implantation. It stays in for up to 10 years.
Levonorgestrel intrauterine system (LNG IUD) is another intrauterine device. This is also a ‘T’-shaped device placed inside the uterus. It releases a small amount of progestin each day to prevent pregnancy. It lasts for 3 to 6 years depending on the device and has a failure rate of 0.1-0.4%.
- Hormone delivery methods
There are several contraceptive methods that work on the principle of regular, controlled delivery of hormones like progestin in the body. These are as follows:
- An implant is inserted under the skin of the upper arm. It is used for up to 3 years with a failure rate of 0.1%
- An injection or shot of progestin is taken every 3 months to prevent pregnancy. It has a failure rate of 4%
- A skin patch placed on the abdomen or buttocks (never on breasts) releases progestin and estrogen into the bloodstream. It is changed every week for three weeks and then not used for the fourth week so that the woman can have her period. It has a failure rate of 7%
- A hormonal vaginal ring also works the same as the patch. A ring is placed in the vagina, which releases progestin and estrogen. It is worn for 3 weeks, removed during the menstruation week, and then a new ring is placed. It has a failure rate of 7%.
- Oral contraceptive pills are taken at the same time every day. They can be either combination pills that release estrogen and progestin or progestin-only pills. They have a failure rate of 7%.
- Barrier methods
These consist of options like a diaphragm, cervical cap, or sponge. They contain a spermicidal and are worn before sexual intercourse. It is placed inside the vagina to cover the cervix and block the sperm. They have a failure rate of 14- 27%.
- Male condoms are worn by the man to prevent the sperm from entering the vagina during vaginal intercourse. Furthermore, they are widely used as they prevent the transmission of STDs and provide birth control. They are made of latex and should be avoided if either of the partners has a latex allergy. They have a failure rate of 13%.
- Also, there are female condoms available for women. They are packaged with a lubricant and have a failure rate of 21%.
- Spermicides are also available as foam, gel, tablets, cream, film, or suppository. They act by killing the sperms. They are placed in the vagina no more than an hour before intercourse and left for 6 to 8 hours after. But they have a failure rate of 21%.
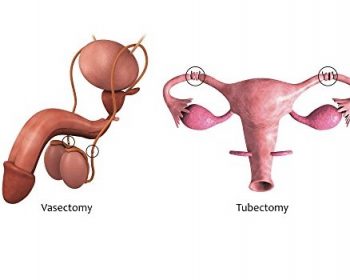
Male and female sterilization are surgical methods of contraception.
For enquiries and online appointments, visit www.DivakarsHospital.com
You can seek 2nd opinion with Dr Hema Divakar and other specialist doctors through the Divakar’s Hospital app which can be downloaded from Google Play Store or ios here – https://bit.ly/2C5cW1e
Subscribe to Divakars Hospital YouTube Channel and stay updated on videos related to pregnancy and women’s healthcare. Subscribe here – https://bit.ly/3Avct4w
Source :