PCOS

Know Everything About PCOS – Blogs By Experts
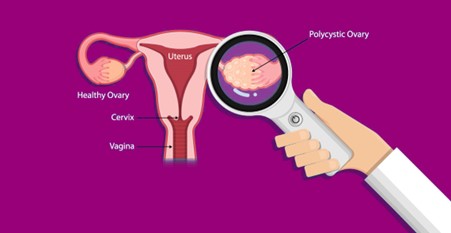
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder found commonly among women of reproductive age. Individuals with PCOS have infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual periods. They also have higher-than-normal levels of the male hormone androgens. Excess of androgens disrupt the normal menstrual cycle and cause irregular periods.
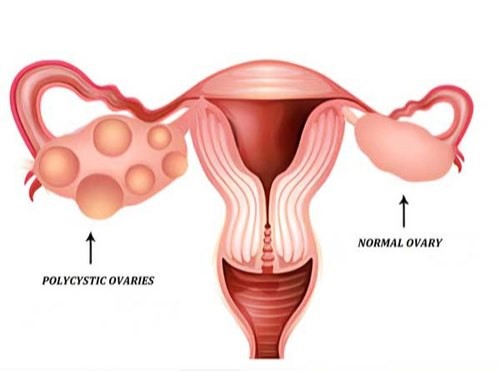
Some individuals also have multiple cysts on their ovaries, leading to the name polycystic syndrome. Although, it is misleading because not every individual diagnosed with PCOS has cysts in their ovaries.

PCOS – Diagnosis and Treatment
There is no definitive test or gold standard to diagnose PCOS. Typically, women are diagnosed with PCOS when they have at least two of the three symptoms listed below:
- High levels of the male hormone, androgens
- Irregular periods
- Multiple cysts in the ovaries
Generally, the doctor starts with a discussion about the medical story, any particular symptom that brings them to the doctor. Any weight changes and the menstrual cycle is also included in this discussion. A physical exam includes checking for any signs of excess hair growth, insulin resistance, or acne.
Management of PCOS
Managing PCOS starts with correctly diagnosing it. Since there is no conclusive test that confirms the diagnosis, many women learn about their PCOS only when they try to get pregnant but cannot. Both these causes make the diagnosis of PCOS difficult.
After being diagnosed, one should always consult a doctor about their specific symptoms and how to best manage them. PCOS is a condition that cannot be treated but can be managed.
Managing PCOS involves lifestyle changes and medication. While the medication for PCOS is prescribed by the doctor, the lifestyle changes are the individual’s prerogative.

PCOS – Causes and Possible Complications
The exact cause of PCOS is not known. There are various factors that are believed to contribute to the symptoms –
- Insulin resistance
- Low-grade inflammation
- Heredity
- Excess androgen
Watch the videos to know about various aspects of PCOS
Videos from Divakars Hospital Youtube Channel
Q&As on PCOS
Who suffers from PCOS?
Women of reproductive age, between 14 to 45 years of age, suffer from PCOS. Around 5% to 15% of women of child-bearing age are diagnosed with symptoms of PCOS. Most women are diagnosed with PCOS when they start menstruating at puberty. Though some others are diagnosed later in life when they gain a significant amount of weight, which makes them obese. A few women might also discover that they have PCOS during their 20s or 30s when they are trying to get pregnant and are unable to, since PCOS is one of the most common causes of female infertility.
Women of all races and ethnicities are at risk of developing symptoms of PCOS. There is a higher risk for women who are overweight or have a family history of PCOS.
Can one still get pregnant after a PCOS diagnosis?
Yes. A PCOS diagnosis does not mean that the individual can never get pregnant. PCOS is one of the most common, yet treatable, causes of infertility in women. The disruption in ovulation due to an excess of the male hormone leads to infertility. This can be treated with some lifestyle changes like a balanced diet, regular exercise, medication, etc. There are infertility treatments like Invitro fertilization (IVF) that can help women with PCOS get pregnant. pregnancies with PCOS can be complicated due to high blood sugar, high blood pressure, higher risk of miscarriages, and premature birth.
Does PCOS go away after menopause?
Since women stop menstruating after menopause, the symptoms of PCOS related to disruption of the menstrual cycle cease but the hormonal imbalance that was causing the symptoms in the first place still exists. Also, PCOS affects various systems in the body. Even when the menstrual cycle-related symptoms cease after menopause, the risks of other PCOS-related health problems such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, endometrial cancer, stroke, etc. increase with age.
So, even though most symptoms of PCOS may go away after menopause but the complications that arise due to the hormonal imbalance, put these individuals in a higher-risk category for other health conditions.
What home remedies can be taken to improve PCOS symptoms?
Steps that can be taken at home individually to improve PCOS symptoms include :
- Losing weight- It should be done by following a balanced, low glycemic index diet. Healthy eating habits combined with regular exercise over a period of time can help reverse the disruption of the menstrual cycle and regulate ovulation. Even a 5% to 10% reduction in weight will help lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin resistance in cells, and correct hormone imbalance.
- Removal of excess, unwanted hair – There are various methods that can be used to get rid of unwanted hair like hair removal products. Other methods like laser hair removal and electrolysis can be taken at a doctor’s clinic. A prescription skin treatment using Eflornithine helps slow the growth of hair.
How does PCOS affect pregnancy?
PCOS can cause problems with pregnancy. It increases the risk of miscarriages, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy), and premature birth. These are considered to be high-risk pregnancies.
What treatment options are available to get pregnant after a PCOS diagnosis?
Treatment options that help with getting pregnant in women with PCOS are:
- Reaching a healthy weight – Attaining a healthy weight helps regulate hormones and ovulation, thereby increasing one’s chances of getting pregnant.
- Medication – Drugs like Clomiphene help with fertility.
- Invitro fertilization (IVF) – IVF treatment is an option for women who are unable to get pregnant despite trying the above measures. In this, the egg is fertilized by the sperm outside (in vitro) and then implanted in the uterus. It has a higher chance of success than most other methods.
- Surgery – Ovarian drilling is a surgery in which a few holes are made on the outer surface of the ovary using lasers or electrocautery. It leads to ovulation for 6 to 8 months.
How to prevent problems due to PCOS during pregnancy?
It is difficult to get pregnant with PCOS. In such cases, even after getting pregnant, it is considered to be a high-risk pregnancy. To prevent problems during pregnancy, women with PCOS should consider a few things before getting pregnant.
- Reach a healthy weight before pregnancy- One should consult with their doctor about attaining a healthy weight that will help them carry their pregnancy without any complications.
- Maintain good blood sugar control – One should consult with their endocrinologist and maintain good glycemic control with a balanced diet, exercise, and medication so that they can avoid gestational diabetes.
- Taking folic acid.
What types of medicine treat PCOS?
Medications prescribed for PCOS mainly aim to manage the hormonal imbalance or a specific symptom.
Birth control pills that contain progestin help restore hormonal balance, regulate ovulation and menstrual cycle, and protect against endometrial cancer. It also comes as a skin patch and a vaginal ring.
Combination birth control pills that contain estrogen and progestin decrease androgen production and regulate estrogen. It helps improve PCOS symptoms. It is also available as a skin patch and vaginal ring.
Metformin is a drug used to treat type II diabetes. Studies have suggested that metformin when taken in addition to a balanced diet and moderate exercise leads to weight loss, lowers blood sugar, and regulates the menstrual cycle.
Various other medications help reduce excess hair growth, like spironolactone, eflornithine.
What are the health problems associated with PCOS?
PCOS is essentially a hormonal disorder. It affects various other systems in the body. Some of the health problems commonly found associated with PCOS are:
- Diabetes – Hormonal imbalance in PCOS causes increased insulin resistance and greater predisposition to type II diabetes. Women with PCOS have a higher risk of developing diabetes with age.
- High blood pressure and cholesterol levels – Low-grade inflammation, generally, found with PCOS puts these individuals at a higher risk for developing cardiovascular diseases like high blood pressure. The hormonal imbalance also increases blood Low-density Lipid (LDL) “bad cholesterol” and decreases blood High-density Lipid (HDL) “good cholesterol”.
- Depression, anxiety, and eating disorders.
- Endometrial cancer – Irregular periods prevent the regular shedding of the uterine lining and this lining, and this buildup can lead to endometrial cancer.
- Obstructive sleep apnea – Obesity associated with PCOS leads to obstructive sleep apnea.
Can PCOS be reversed?
No, PCOS cannot be treated, but it can be managed very well. One can learn to live with it. It can be changed from being a lifestyle hampering condition to a more manageable condition.
Now stay in constant touch with expert Gynaecologists